The USSR was satisfied that army confrontation with Nazi Germany was unavoidable. But it did all the pieces attainable to delay it.
Practically from the second it was based, the Soviet Union started to arrange for the brand new world struggle that the nation’s management believed was inevitable. A significant confrontation with the capitalist West promised to be brutal, bloody and uncompromising.
Under Soviet army doctrine, the Red Army was to resist an preliminary enemy assault, defeat the enemy in border battles, launch a large-scale counter-offensive and obtain decisive victory, thereby safeguarding “the peaceful labor of the great family of the multi-ethnic nation”.
Red Army carries out army train.
Alexander Ustinov/russiainphoto.ru
“The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics will respond to any enemy attack with a crushing blow using the entire might of its Armed Forces…” acknowledged the 1939 Field Manual of the RKKA (‘Workers’ and Peasants’ Red Army’). “If the enemy foists war on us, the Workers’ and Peasants’ Red Army will be the most attacking army of all the armies that have ever attacked. We will wage war offensively, taking it to the enemy’s territory. The Red Army’s military operations will be targeted at annihilation, aiming to totally destroy the enemy.”
Cadres are all the pieces
For a rustic that had lived by a devastating Civil War and international intervention, modernization of its Armed Forces was a particularly essential, however very troublesome job. Reform and a rearmament of the military on a big scale was in massive measure made attainable by the industrialization that the USSR launched in 1929.
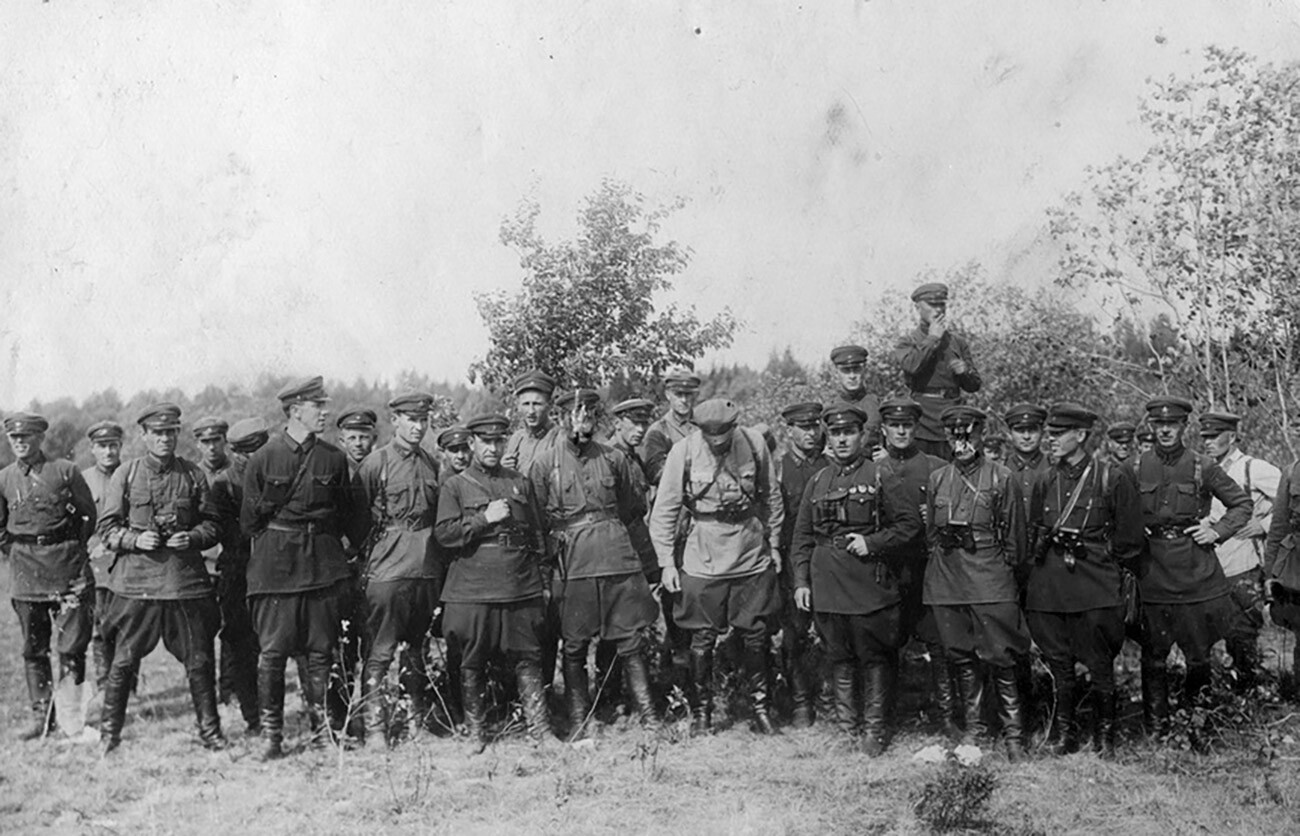

Soviet troops perform army train.
Andrey Malygin’s archive/russiainphoto.ru
Because of financial issues, for a very long time, the Red Army was organized in keeping with the territorial militia precept of recruitment: Those eligible for army service underwent a brief interval of army coaching close to their locations of everlasting residence, whereas the variety of common servicemen (primarily command personnel) was minimal. In the second half of the Nineteen Thirties, the military was moved to a full-time common footing, which was conclusively enshrined within the Law on Universal Military Service in 1939.
The Red Army, which numbered 1.9 million on the eve of World War II, had grown to 5 million by the point of the Wehmarcht’s invasion of the Soviet Union on June 22, 1941. The course of of multinational of latest models and formations was properly beneath approach. Thus, the variety of divisions alone elevated from 98 to 303. Such a speedy development couldn’t however result in organizational issues, a scarcity of command personnel and a deterioration of their high quality.
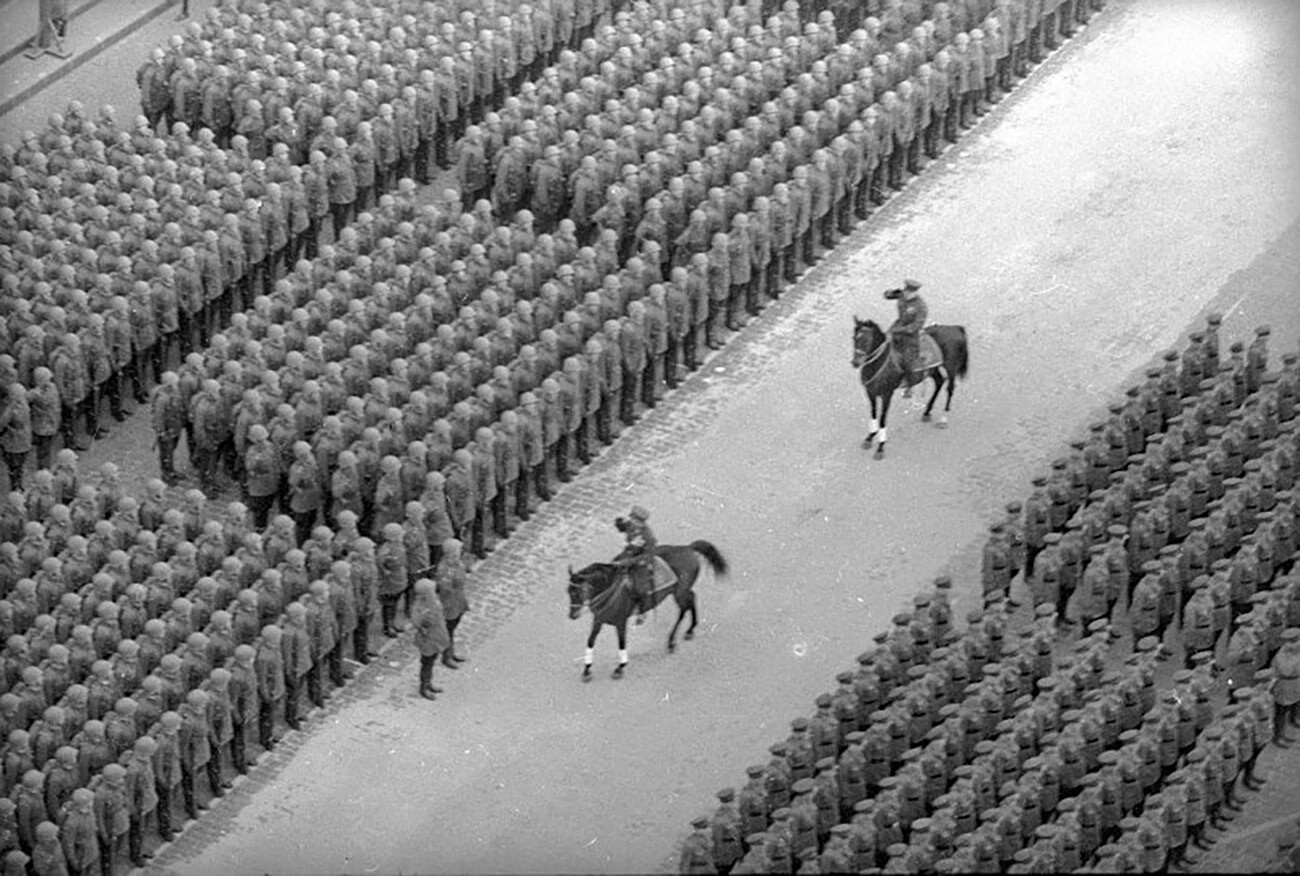
Military parade on Red Square.
Emmanuil Evzirikhin/МАММ/МDf/russiainphoto.ru
The mass purges of 1937-1938, which affected tens of hundreds of individuals to 1 diploma or one other, additionally dealt a particularly painful blow to the command personnel of the Red Army. Only two of the primary 5 Marshals of the Soviet Union had been nonetheless alive by the Spring of 1939.
The penalties of the ‘Great Terror’ clearly manifested themselves throughout the 1939-1940 Winter War towards Finland, which was extraordinarily troublesome for the Soviet troops. After its conclusion, the management of the Armed Forces underwent a significant reshuffle and plenty of commanders who had been prosecuted for political causes, together with the long run Marshal Konstantin Rokossovsky, returned from jail and rejoined the troops.
‘The armor is powerful and our tanks are quick’
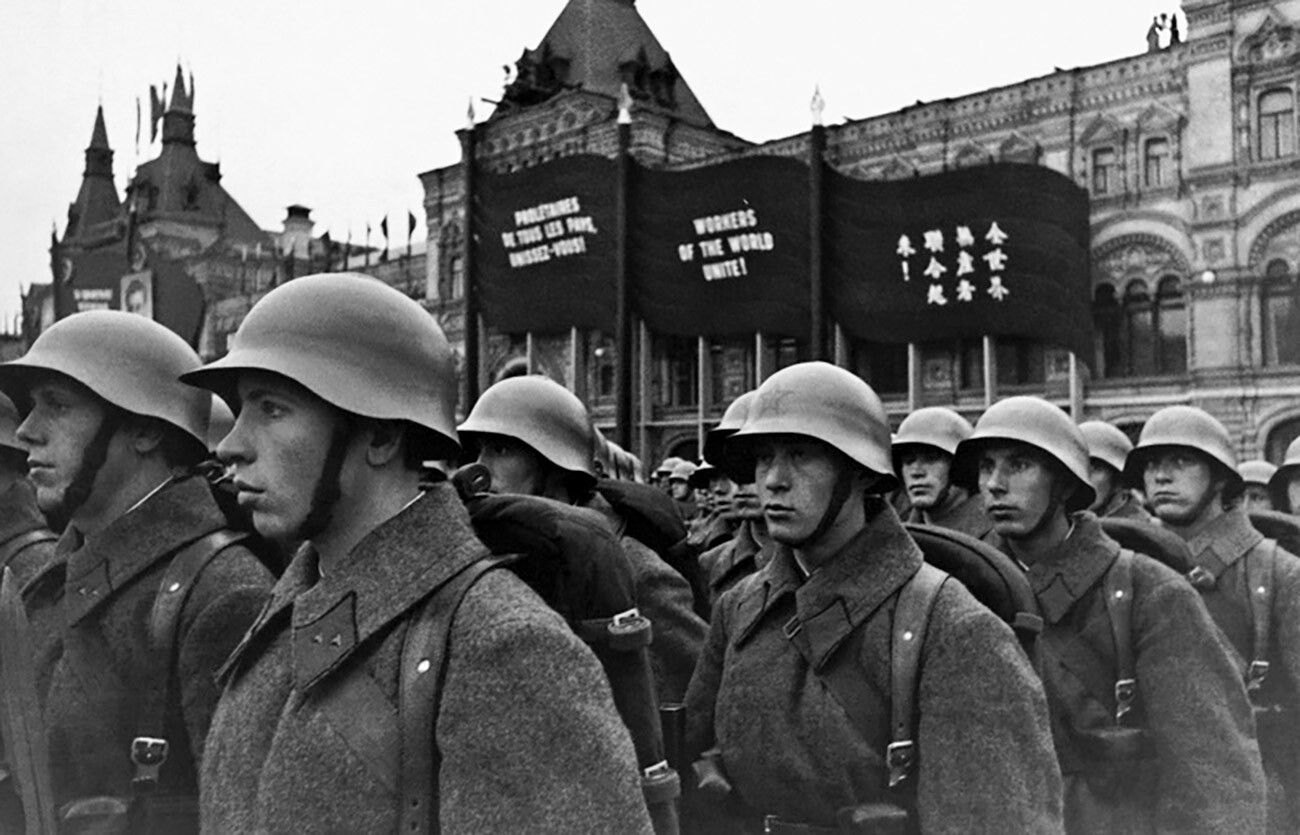

Military parade on Red Square marking the twentieth anniversary of Great October Revolution, 1937.
The State Museum of Political History of Russia
In the years main as much as the struggle, the provision of {hardware} to the Red Army proceeded at a blistering tempo. Between 1939 and 1941, the variety of tanks within the Red Army elevated from 10,000 to 25,000 (together with coaching fashions), fight plane from 5,000 to 14,000 and subject artillery from 34,000 to 91,000 weapons.
Among the latest weapons being equipped to the armed forces had been the Tokarev self-loading rifle (SVT-40), the Shpagin machine pistol, the 76-mm divisional subject gun, the 122-mm howitzer, the 85-mm air protection gun, the T-34 medium tank, the KV-2 heavy tank, the Yak-1 and MiG-3 fighter planes, the Il-2 ground-attack aircraft and likewise the Pe-2 dive bomber.
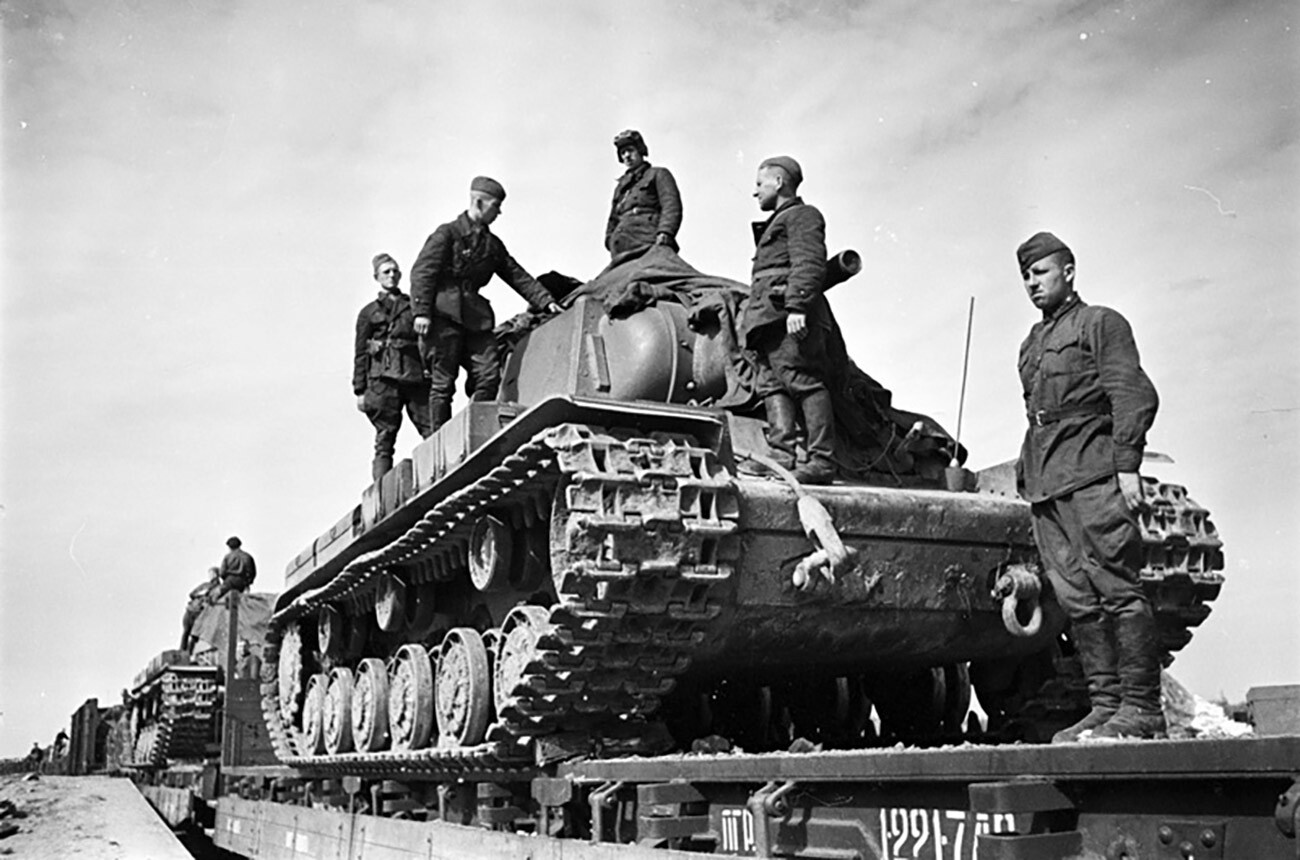

Soviet tanks on the best way to the entrance.
Arkady Shaikhet/russiainphoto.ru
By the Summer of 1941, nonetheless, the share of contemporary {hardware} within the armed forces was nonetheless very low, whereas even older fashions had been typically in brief provide, too. “During the march, I observed despairingly our antiquated T-26, BT-5 and rare BT-7 tanks, realizing they would not be able to endure extended combat. And that’s without noting that we had no more than one-third of the establishment level of even these tanks,” recalled Konstantin Rokossovsky, who commanded the ninth Mechanized Corps within the first days of ‘Operation Barbarossa’.
Up to 40 % of the army finances was being spent on the event of the Soviet air power in 1940. MiG-3 and LaGG-3 fighter planes, which, by way of efficiency traits, had been able to holding their very own towards their Luftwaffe counterparts, had been already in service by the beginning of the battle. But their manufacturing was solely simply getting beneath approach in 1941 and the overwhelming majority of fighter planes had been nonetheless the previous fashions.

Military plane inspection.
Evgeny Khaldey/МАММ/МDF/russiainphoto.ru
The army conflicts towards the Japanese and the Finns within the late Nineteen Thirties, from which the army management drew the suitable conclusions, performed an essential half in elevating the nation’s protection capabilities. Thus, inter alia, after the conclusion of the Winter War, the USSR boosted manufacturing of mortars and submachine weapons many instances over, their position having beforehand been undervalued.
The ‘Stalin Line’
The plan was for the multimillion-strong and properly armed Red Army to satisfy and smash the enemy on ready defensive positions alongside the Soviet border. Construction of a community of fortified districts in Byelorussia, Ukraine, the Pskov Region and in Karelia started in 1928. These districts could be recognized subsequently because the ‘Stalin Line’.
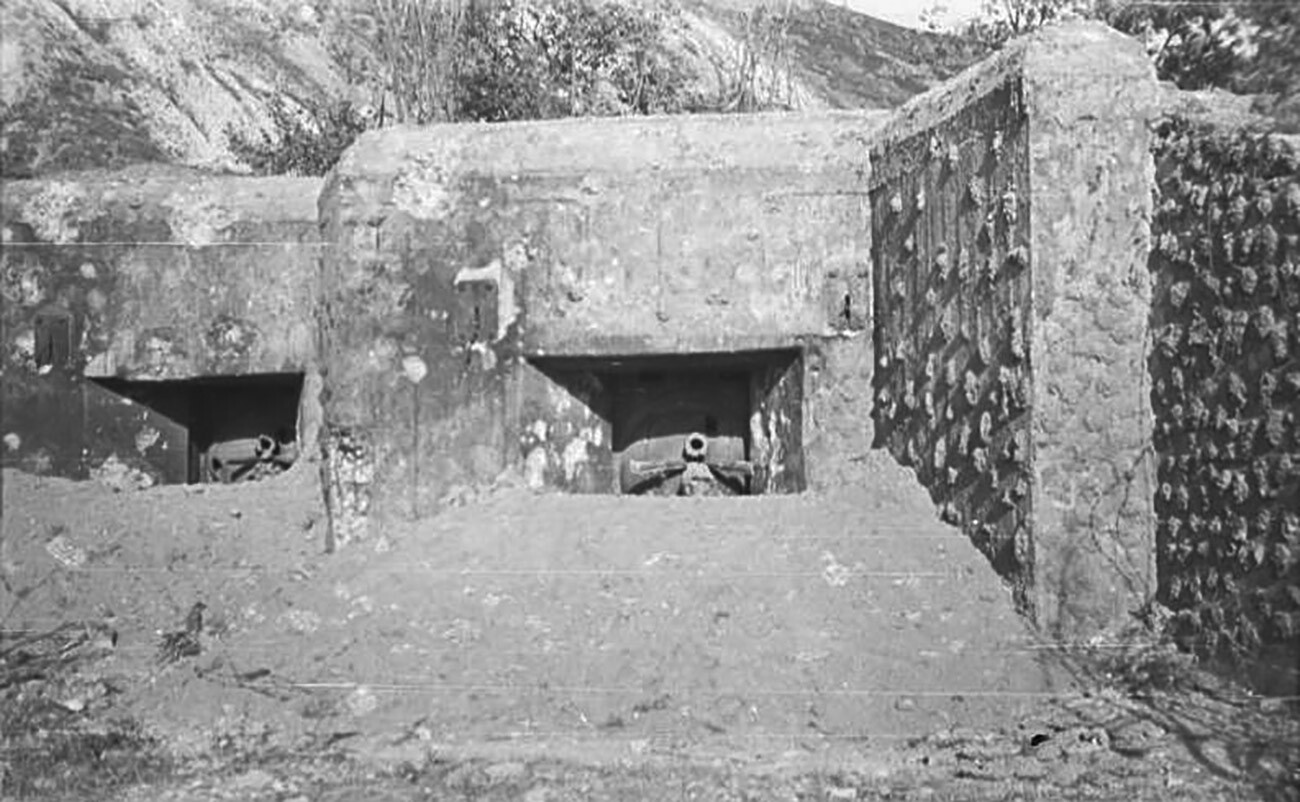

Fortified district of the ‘Stalin Line’.
Bundesarchiv
Each fortified district consisted of a system of interconnected strongpoints positioned within the path of an anticipated enemy offensive. The models deployed in defensive positions right here had machine weapons and anti-tank and caponier artillery at their disposal.
The 1,835-km lengthy ‘Stalin Line’ was twice the size of the Maginot Line, however was noticeably inferior to it, by way of the variety of fight buildings. Because of the massive distances, the fortified districts had nearly no chance of coordinating their actions with each other.
After the USSR’s absorption of Western Ukraine and Western Byelorussia in 1939 after which the Baltic states in 1940, the Soviet border was moved a whole bunch of kilometers to the west. Construction of the ‘Stalin Line’ was suspended and the defensive buildings had been mothballed.
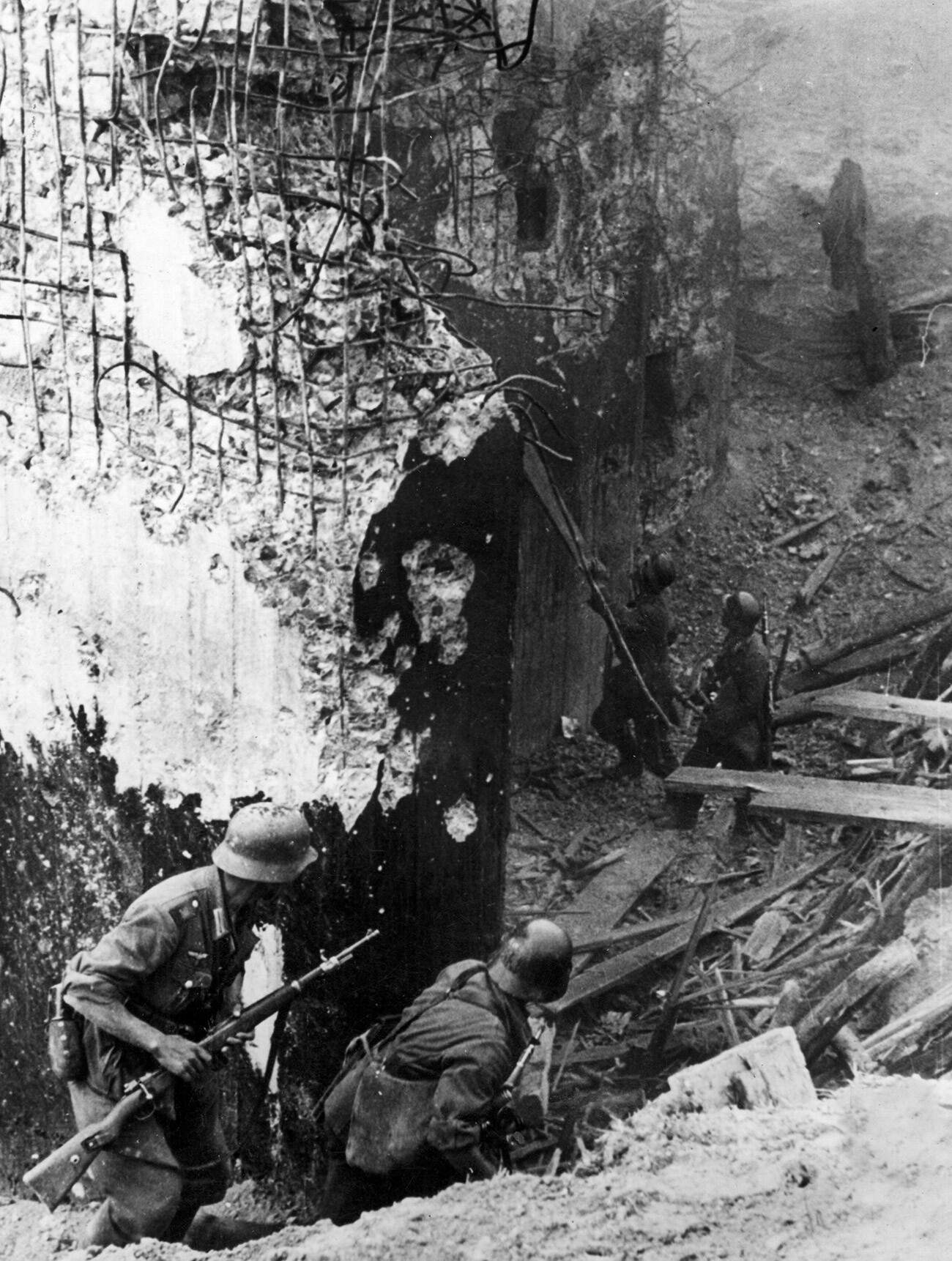

German troopers standing on the entrance of a bunker on the ‘Stalin Line’ destroyed with explosive costs, July 1941.
Mondadori/Getty Images
Construction of fortified districts started on the brand new border, however, by the beginning of ‘Operation Barbarossa’, they’d been 20 % accomplished at greatest and will do nothing to hinder the enemy’s advance.
At the identical time, the “veteran” defenses, which had been swiftly introduced again to life, did, a method or one other, handle to point out their price. Even if the tenacious protection put up by the troopers of the Red Army within the fortified districts of the ‘Stalin Line’ solely succeeded in holding up the Germans for a number of days, this often gave their comrades treasured time to withdraw and keep away from being surrounded.
The Sebezh fortified district held out for a full 10 days and the enemy solely managed to take it by assailing it from the rear. The Karelian fortified zone, in flip, remained one of many key factors within the protection of Leningrad till the blockade was lifted in 1944. It was the place the Finnish military which had superior on town from the north was stopped.
Winning time
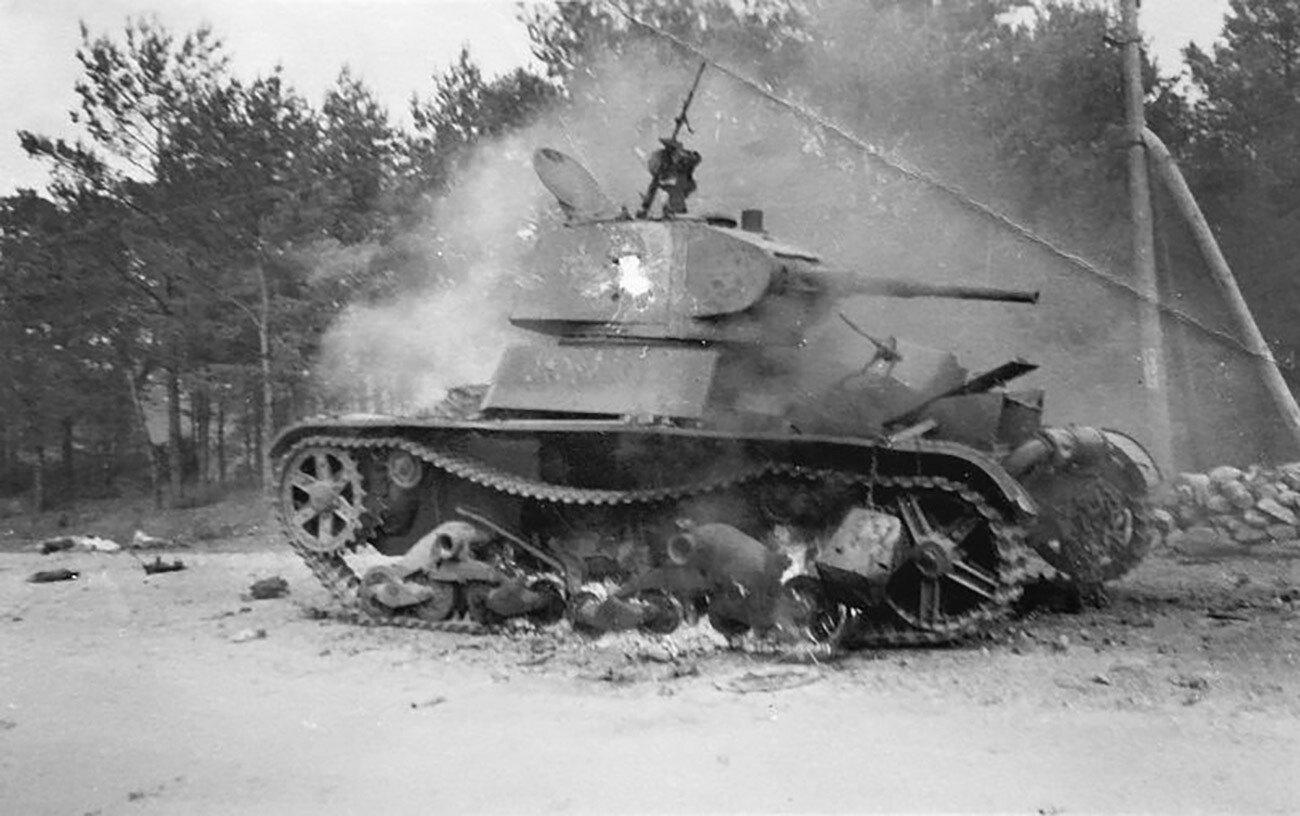

Burining Soviet T-26 tank.
Archive picture
Despite the Soviet Union’s accelerated preparations for struggle towards Nazi Germany, within the inevitability of which no-one had any doubt, a plethora of issues remained unresolved by the point it broke out.
Surpassing the Wehrmacht in tank and aircraft numbers, the Red Army actually did look spectacular, however, on the similar time, many formations proved under-equipped in these classes of {hardware}. They additionally lacked haulage and transport tools and this considerably decreased their mobility.
By the beginning of the struggle, fairly quite a few subdivisions had not undergone applicable army coaching, had not rehearsed operational coordination and had been experiencing a extreme scarcity of junior command personnel – the army faculties merely couldn’t flip them out on the required price for the quickly increasing military. On prime of this, there have been catastrophic issues with the supply of radio communications within the models, and poor group of the work of HQs and the command and management of troops.
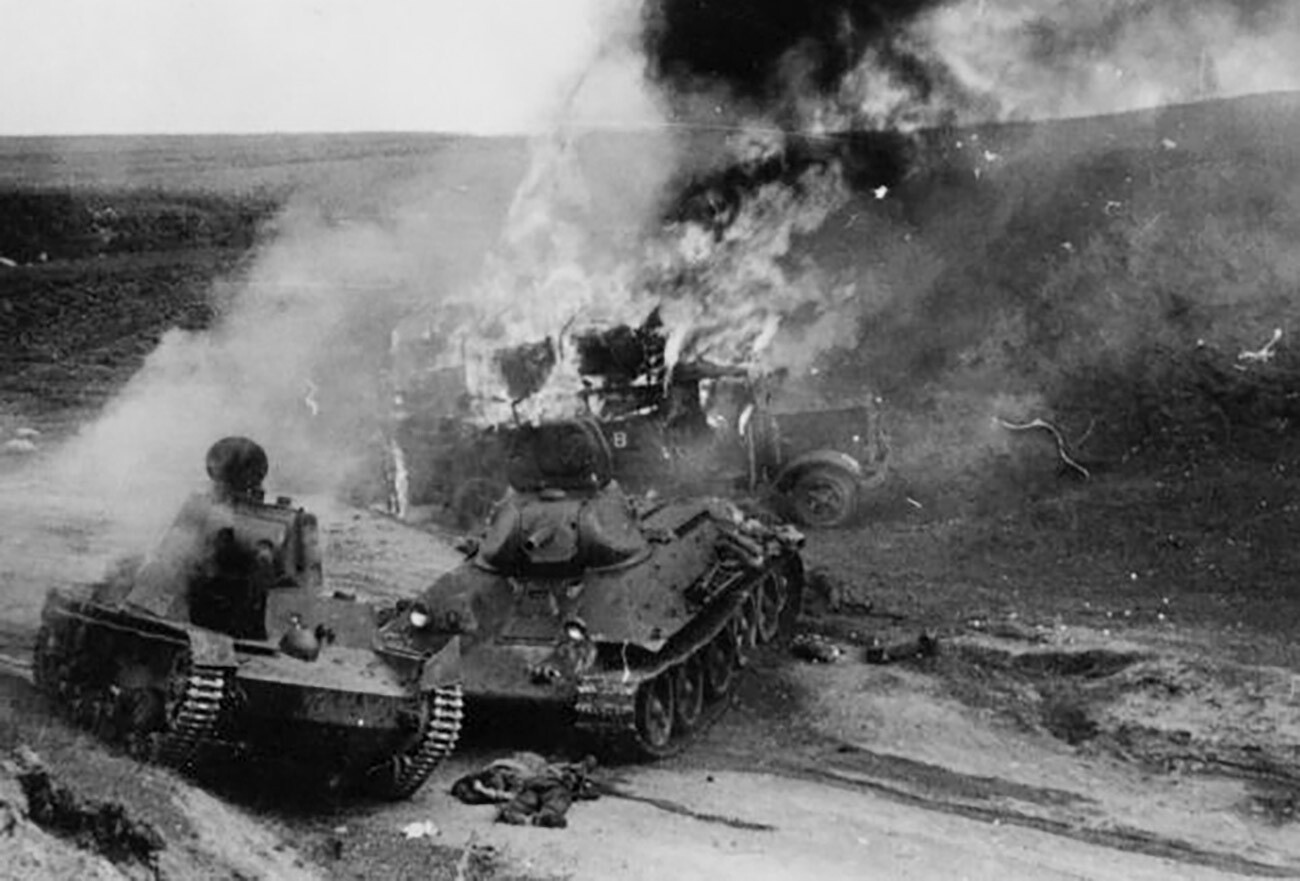

Destroyed Soviet ХТ-130 flamethrower tank and T-34 tank, June 1941.
Archive picture
The Soviet management was by and huge conscious of the day-to-day issues and strove to push again the beginning of the battle by at the least a yr. Border guards and servicemen of models deployed on the border had been ordered in any respect prices “not to yield to provocations”.
In a dialog with the deputy individuals’s commissar for protection, Kirill Meretskov, in February 1941, Stalin remarked: “We won’t, of course, succeed in staying out of the war until 1943. We’ll be drawn into it, whether we like it or not. But, it can’t be ruled out that we’ll stay out of the war until 1942.”
Many of the packages for the reorganization and rearmament of the bottom troops, air power and navy had been slated for completion in 1942 and, within the Summer of 1941, these packages had been in full swing. The USSR was in nice want of a delay, however, ultimately, it was not destined to get it.


