TOKYO, Sep 18 (News On Japan) –
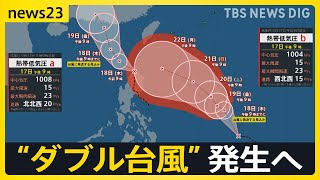
[07:41] Tropical depressions south of Japan are anticipated to strengthen Thursday [September 18th] with heavy rain warnings issued for Kanto and Koshin areas from noon onward.
Sudden downpours struck Tochigi Prefecture on Wednesday night, with sturdy winds and lightning lowering visibility and halting vehicles. Heavy, localized rains additionally hit Fukushima, Fukuoka, and Hiroshima, inflicting flooding, energy outages, and harm to outside tools. Forecasters warn that elements of Kanto might face warning-level rainfall by the evening of September 18th, requiring vigilance in opposition to sudden storms.
Meanwhile, the persistent summer season warmth has raised well being dangers and dealt a heavy blow to agriculture. A U.S. analysis company reported that Japan skilled a median of 62 days this summer season with dangerously excessive temperatures, about one-third attributed to international warming. Tokyo recorded 66 days above threat thresholds, whereas Osaka reached 62. The highest was 70 days in a single metropolis.
Citrus farmers in Shizuoka have been notably hard-hit. Extreme dryness adopted by sudden heavy rains has prompted mandarin oranges to separate open earlier than harvest. “The skin doesn’t have time to expand, so the fruit just bursts,” one farmer defined whereas inspecting broken crops.
In response, some growers are diversifying into climate-resilient crops similar to avocados, generally known as the “butter of the forest.” One Shizuoka farmer famous, “It’s sad to see citrus crack, but these trees love the heat. Seeing them thrive gives us balance.” Farmers hope the primary avocado harvest will come subsequent yr, with expectations rising that new crops might assist maintain agriculture in an period of local weather change.
Japan additionally noticed document numbers of areas exceed 40°C this summer season, with 30 factors throughout the nation breaking the edge. The Meteorological Agency is contemplating a brand new time period to explain such “dangerous heat,” past the prevailing label of “extremely hot days,” to higher convey the dangers posed by intensifying local weather change.
Source: TBS